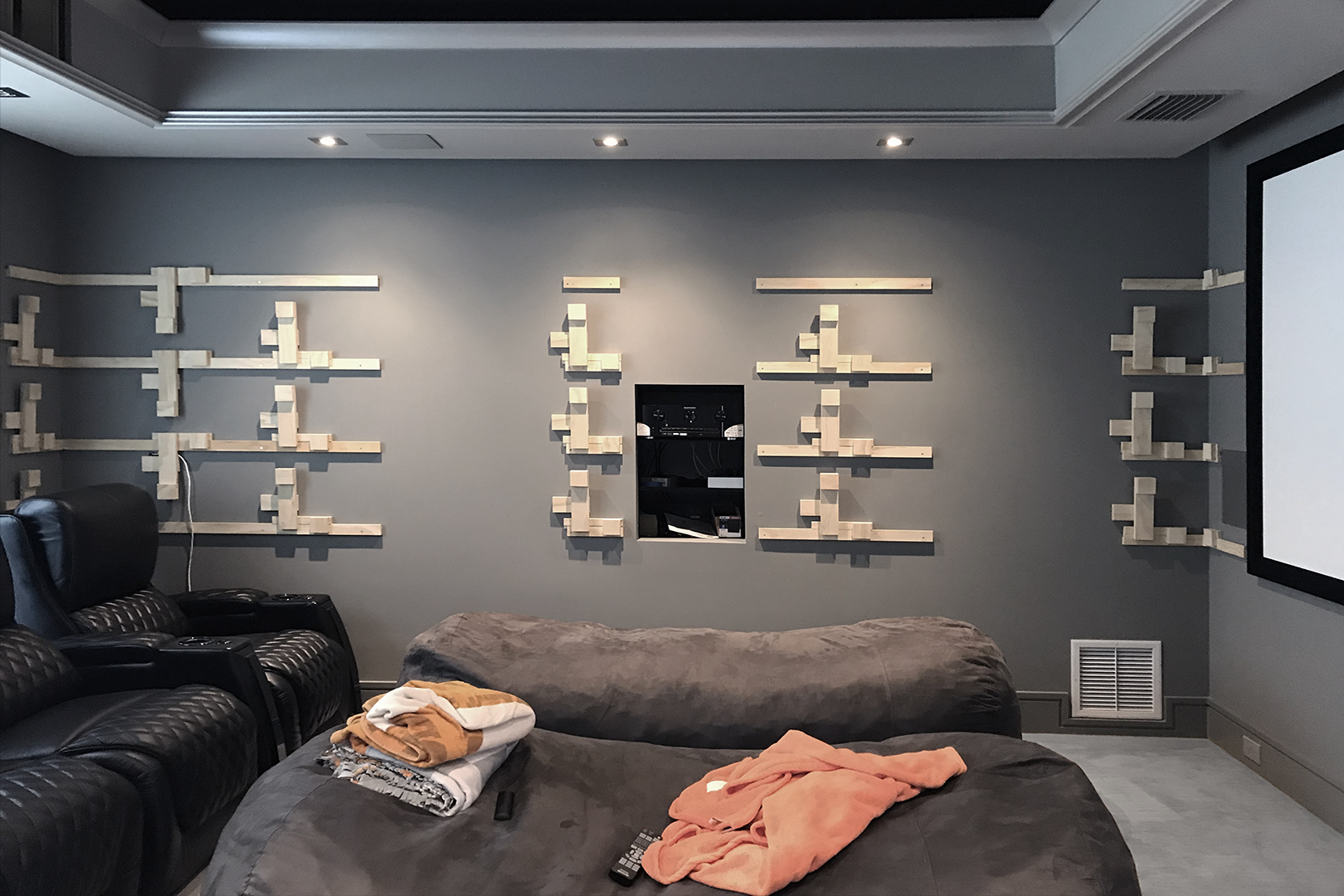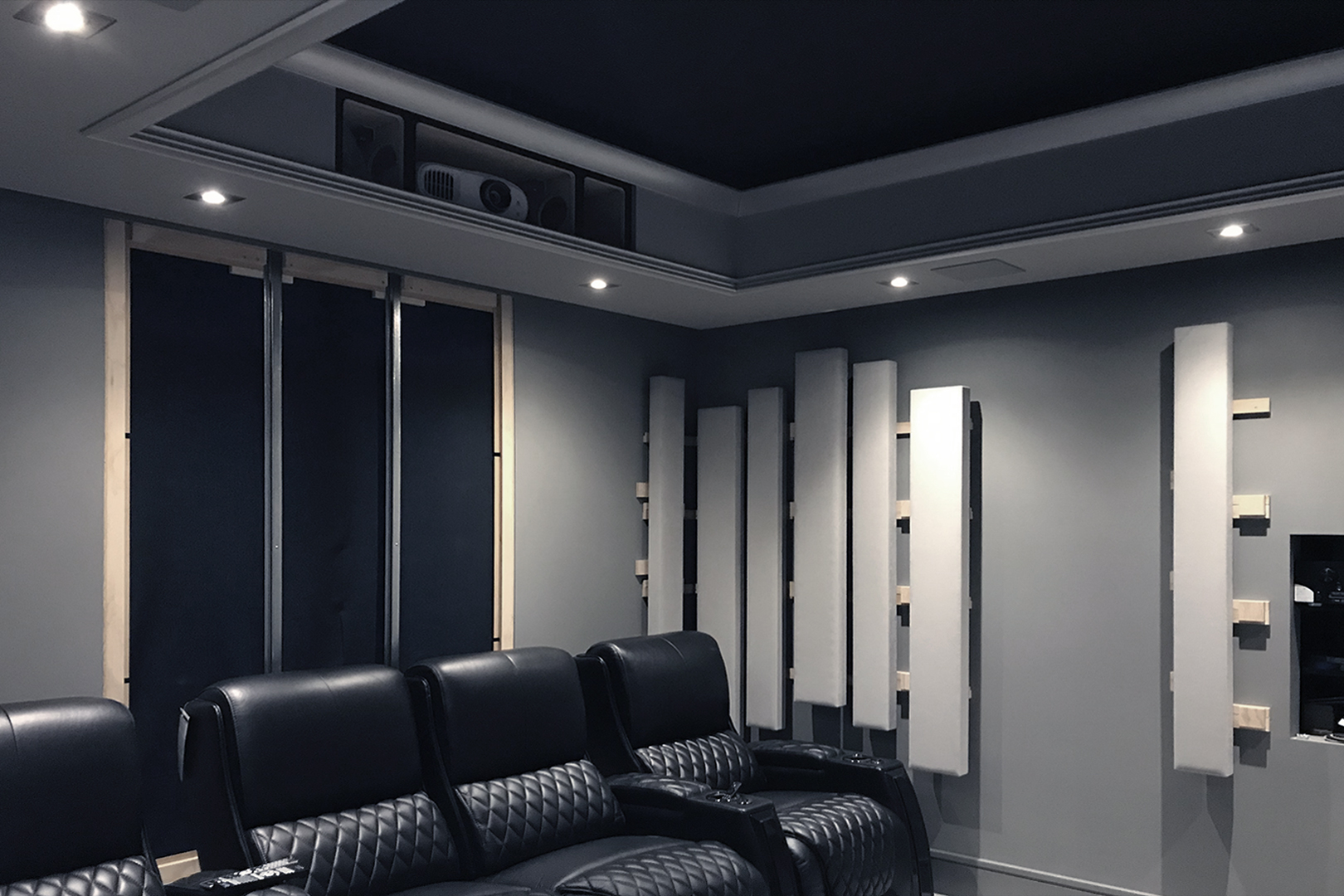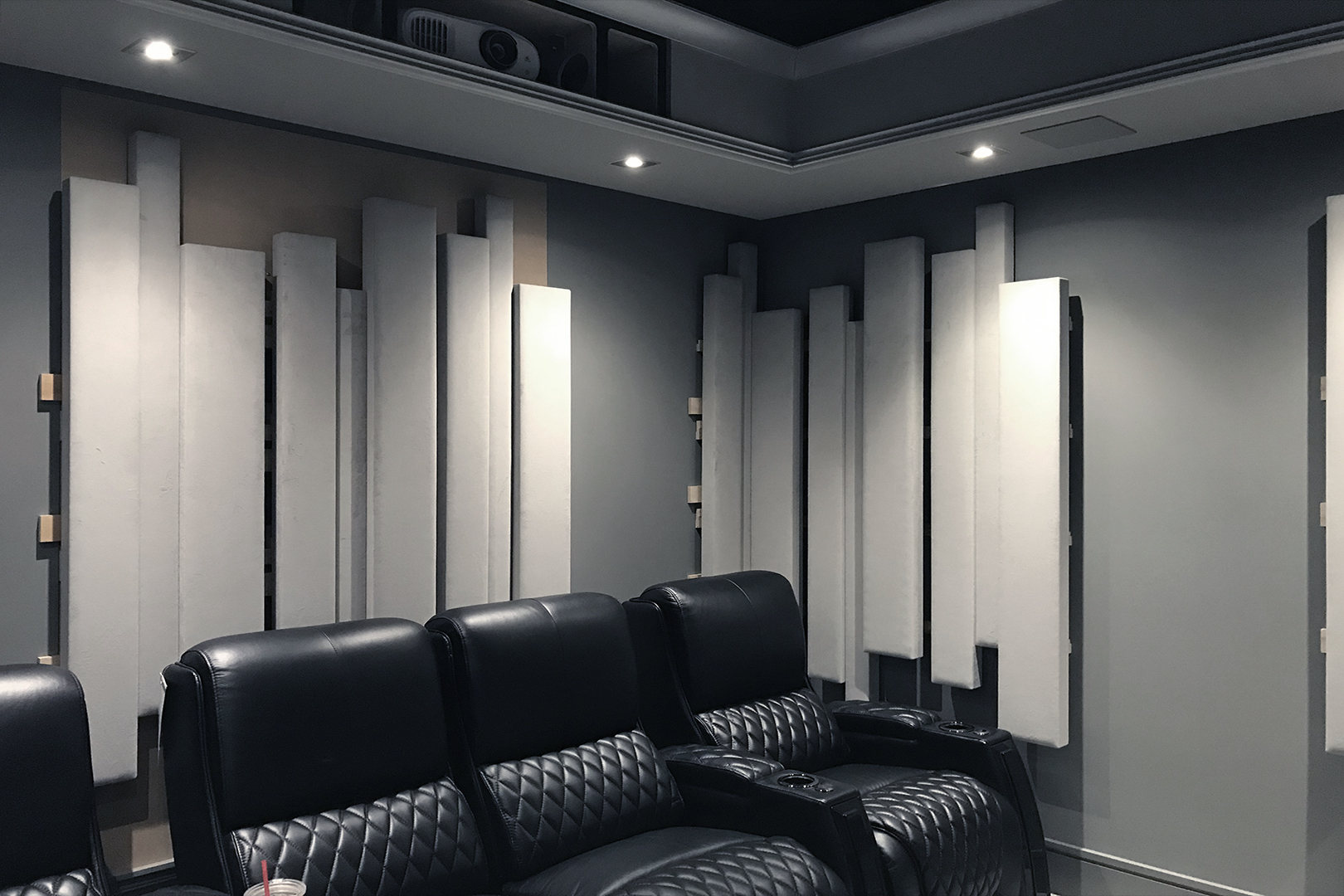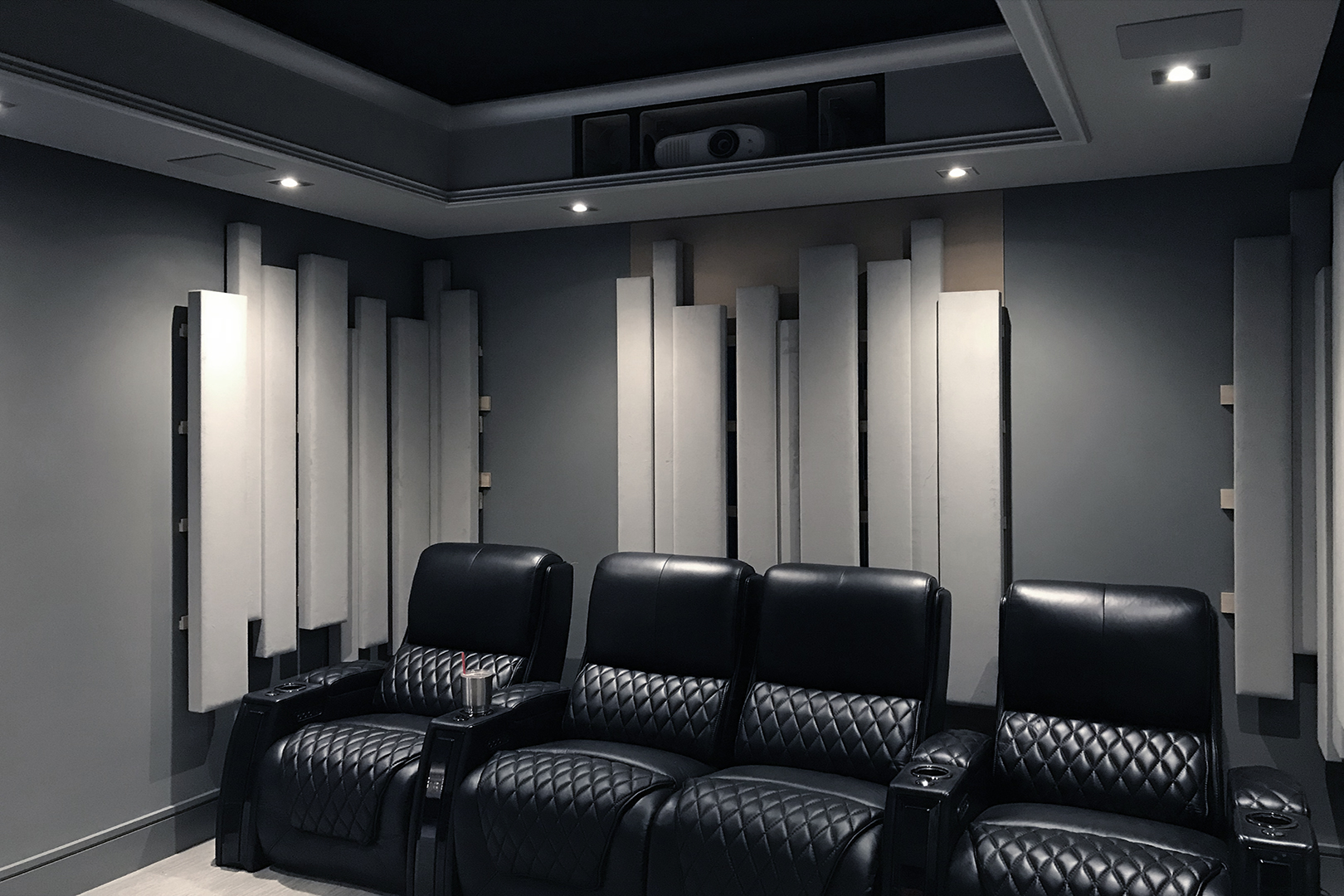

Insight

Connect

vCard

vCard Info
Company Acoustical Artistry
Phone + 1 (407) · 535 · 3121
Email info@acousticalartistry.com
Web www.acousticalartistry.com
Social acousticalartistry
Phone + 1 (407) · 535 · 3121
Email info@acousticalartistry.com
Web www.acousticalartistry.com
Social acousticalartistry
Copy and Paste
Company - Acoustical Artistry
Phone - +1 407 535 3121
Email - info@acousticalartistry.com
Web - www.acousticalartistry.com
Social - acousticalartistry

Affiliates
Page in Development

Affiliates
Page in Development

Shop
Page in Development

FAQs

Our Story
Page in Development

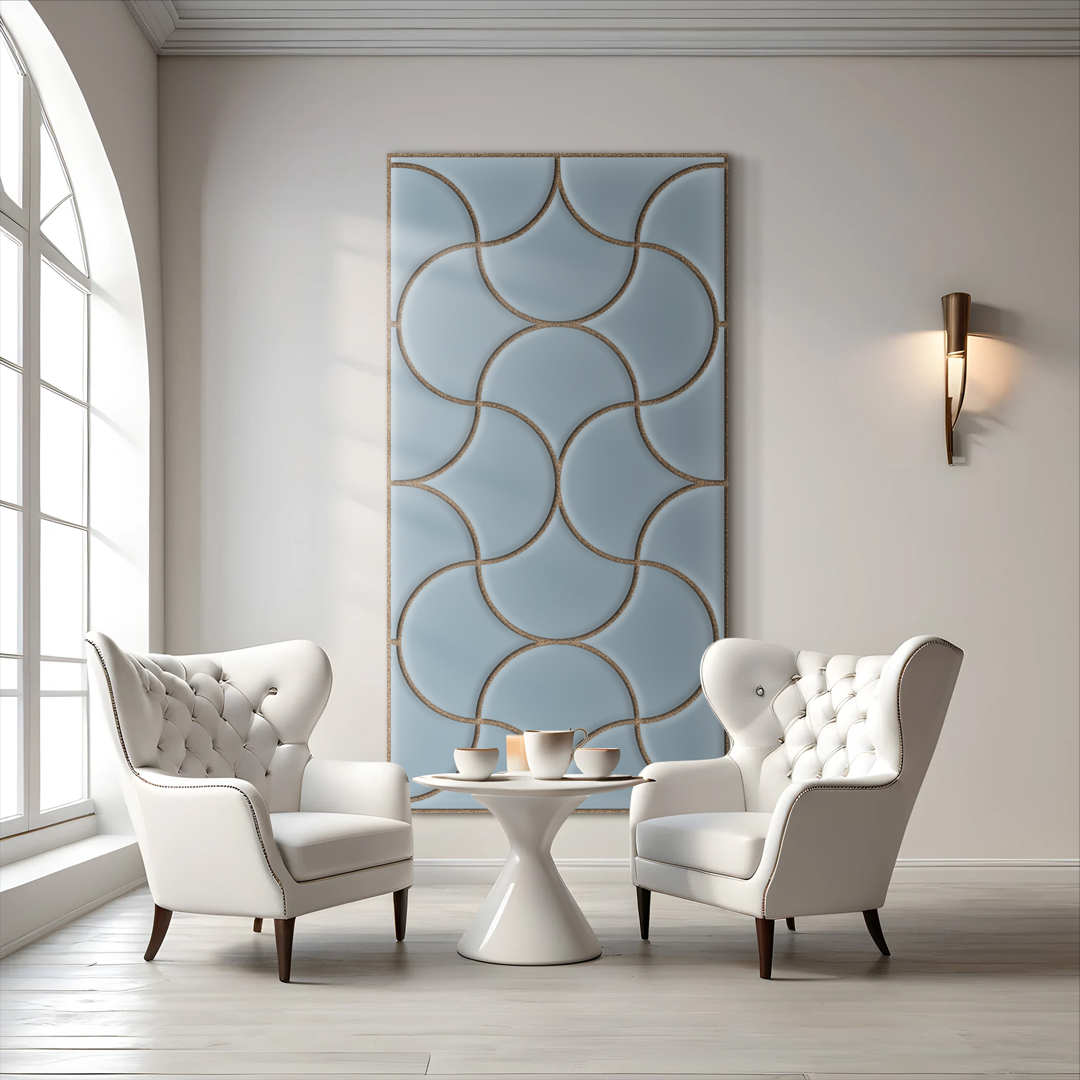
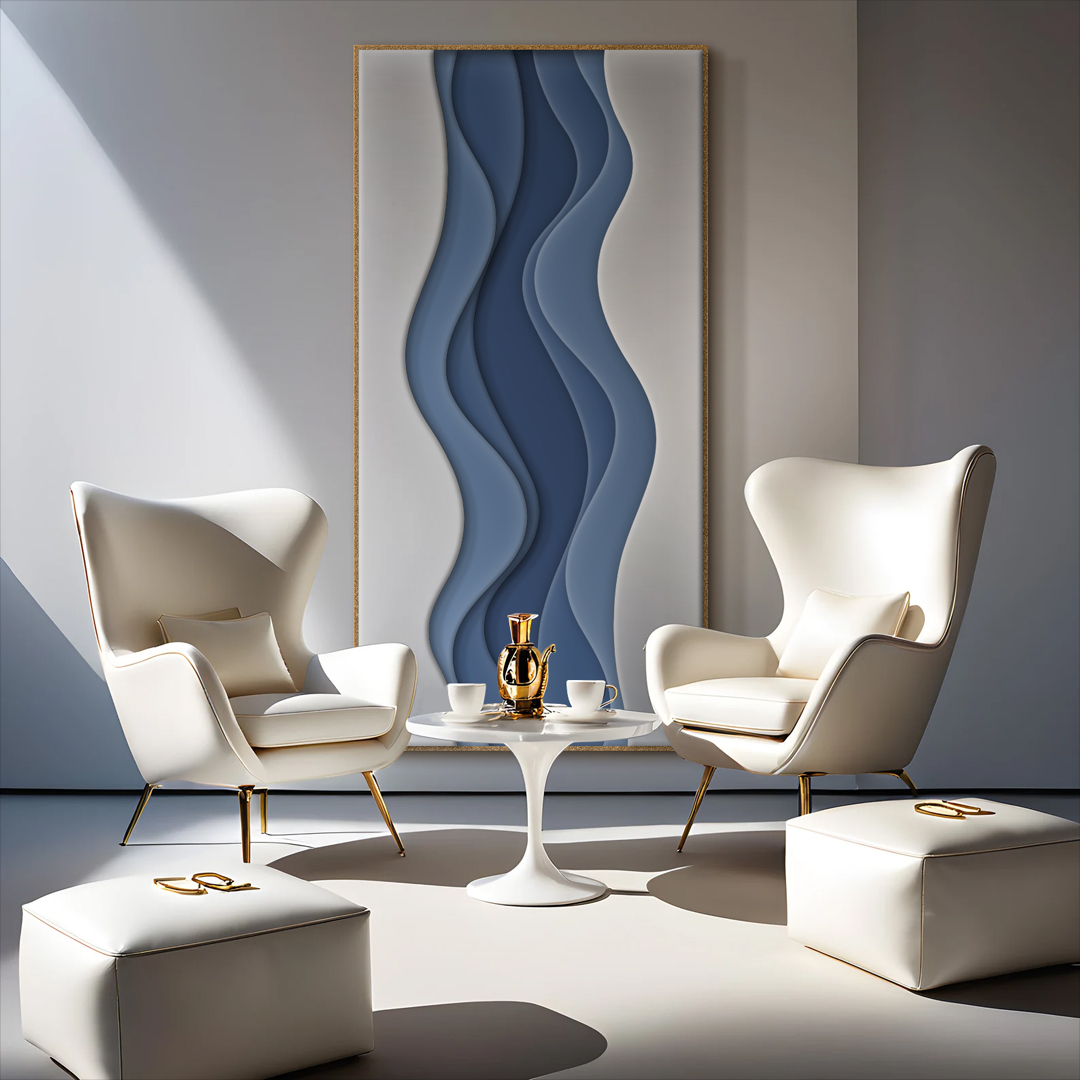
Design

Craftsmanship

Applications

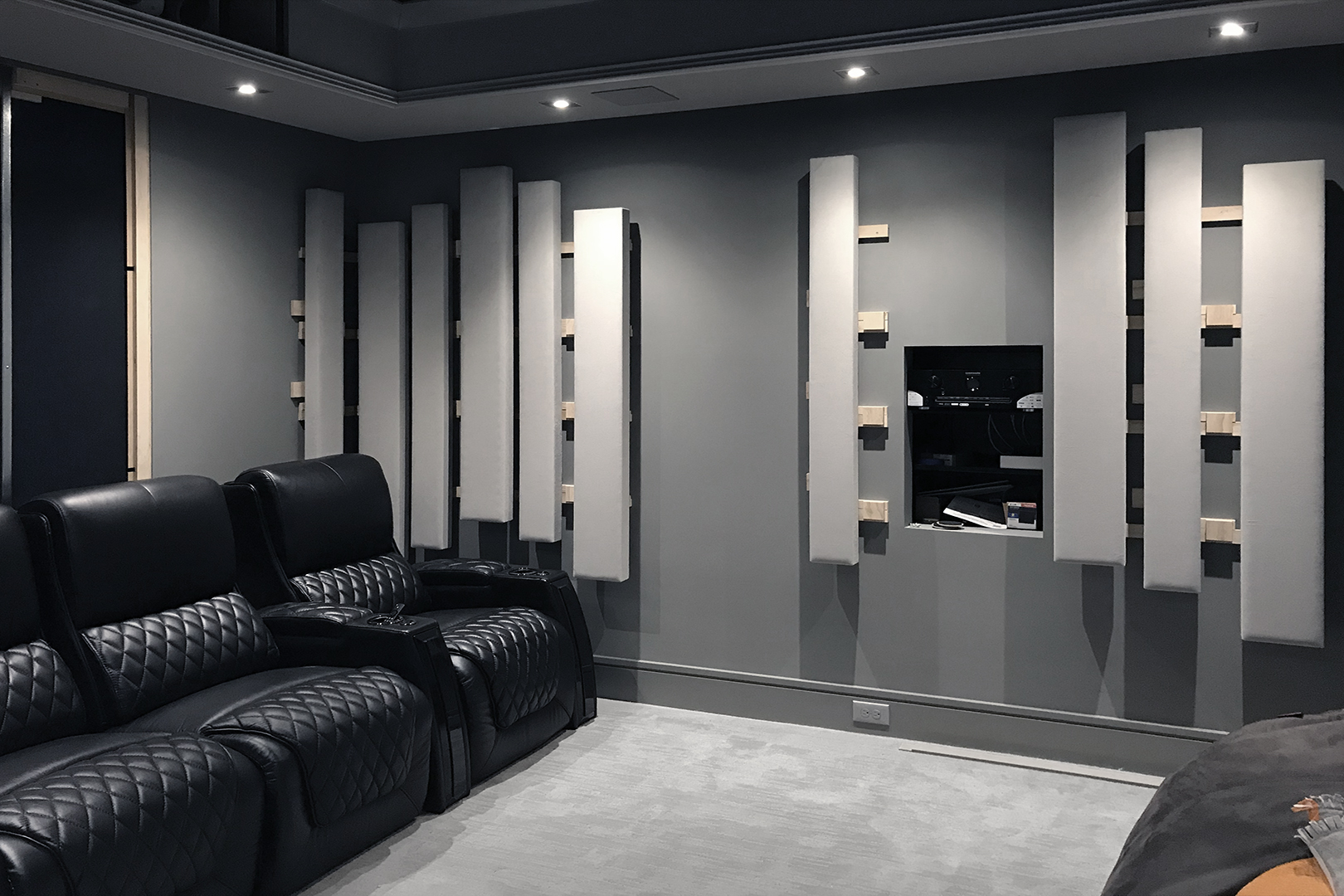
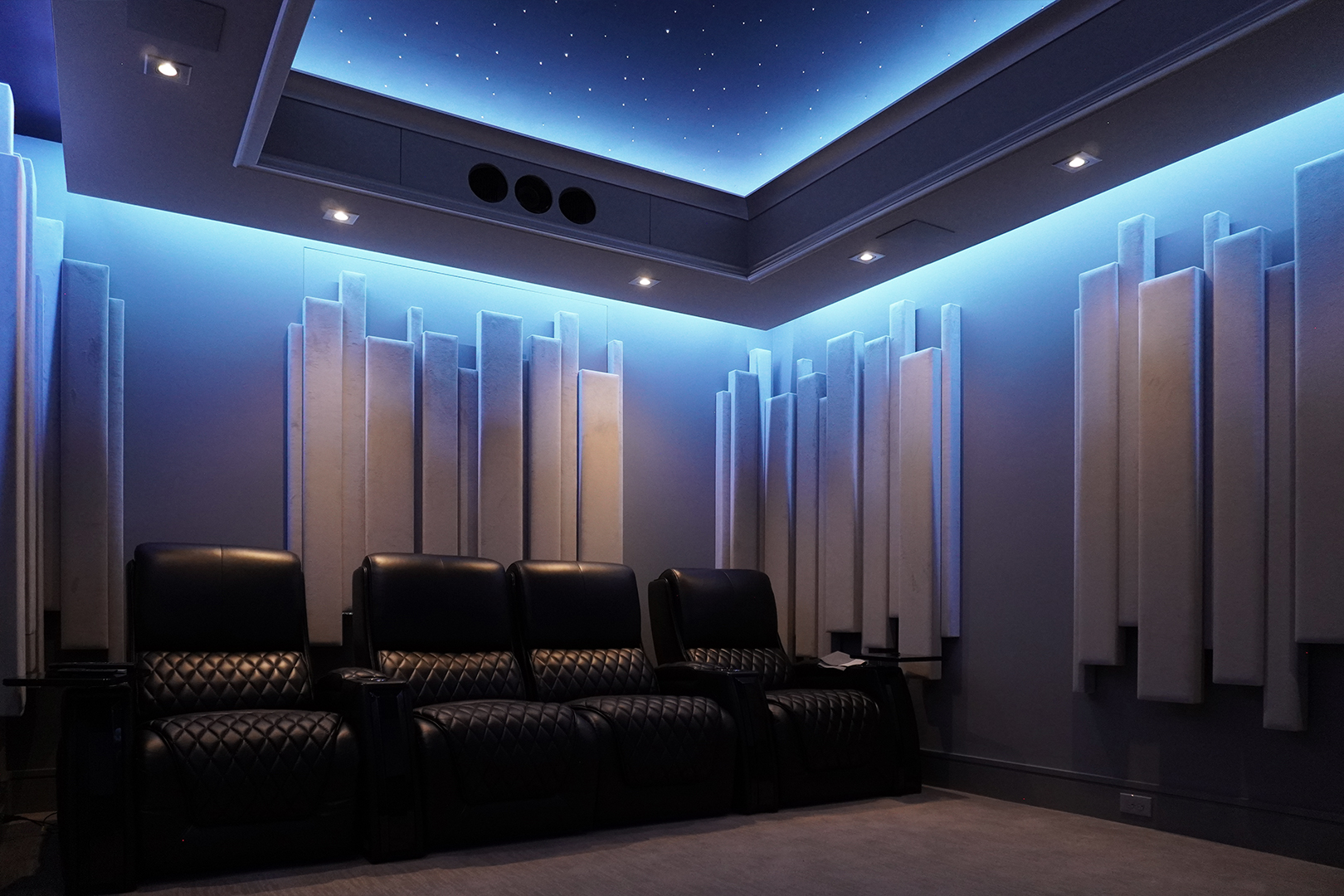
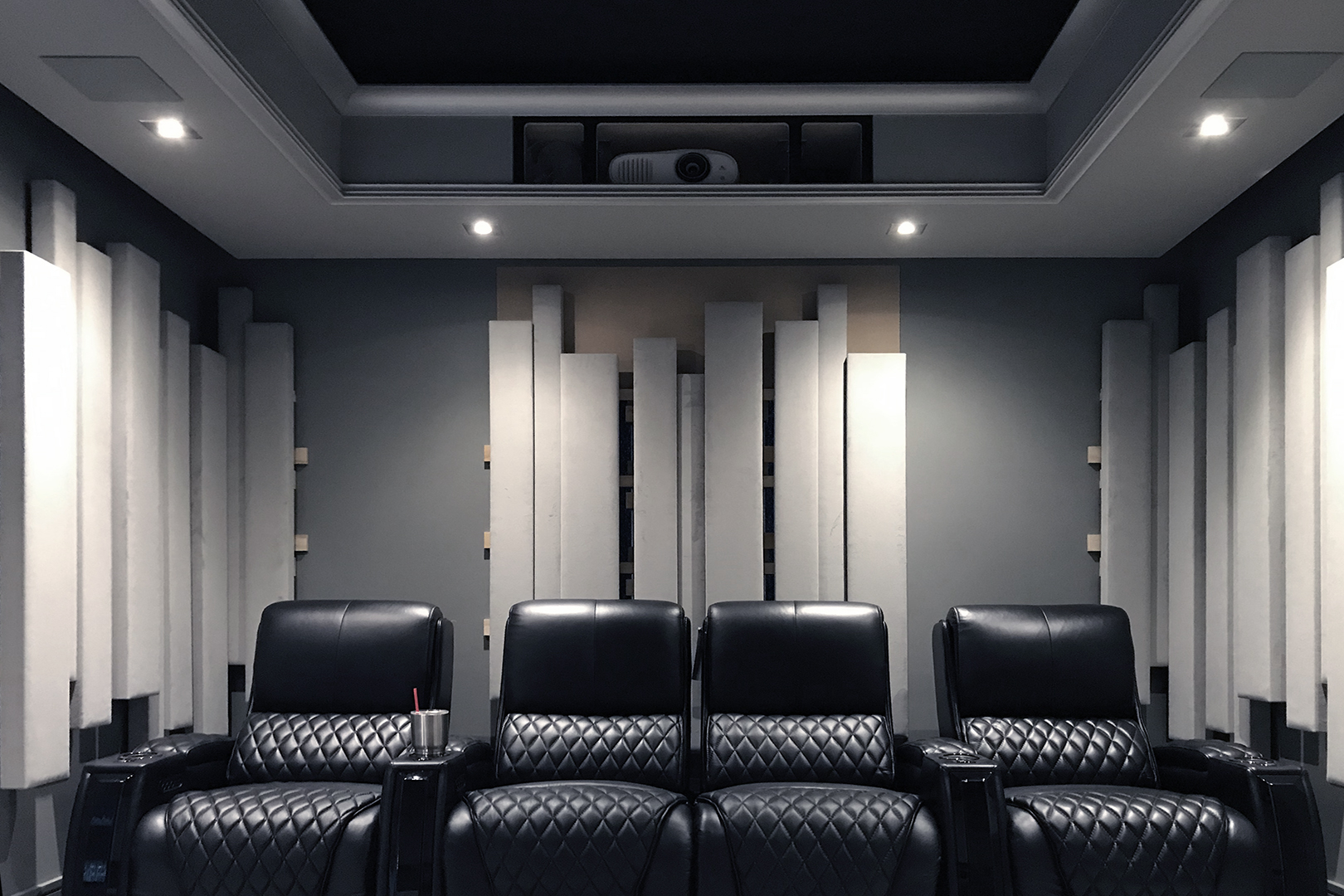
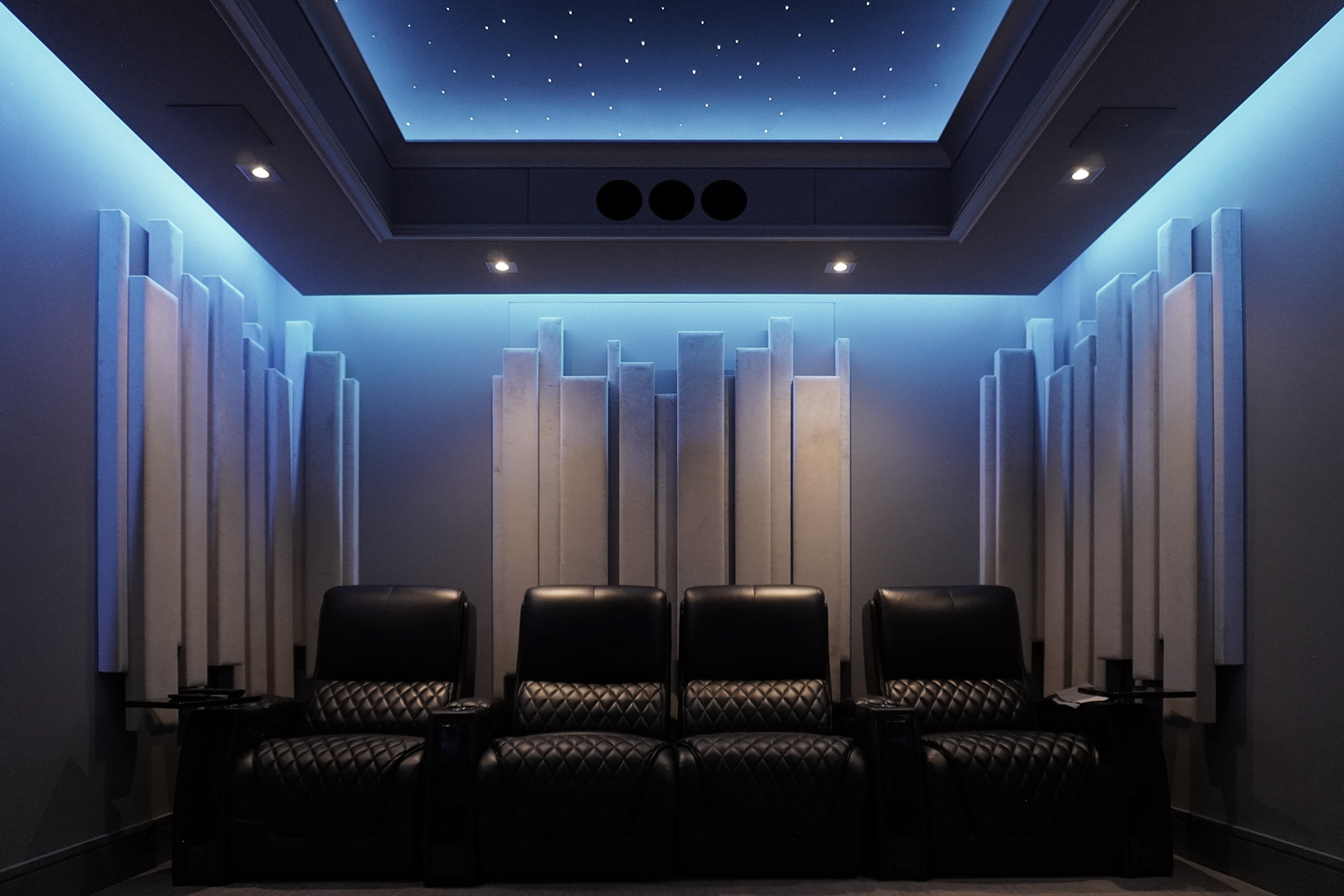
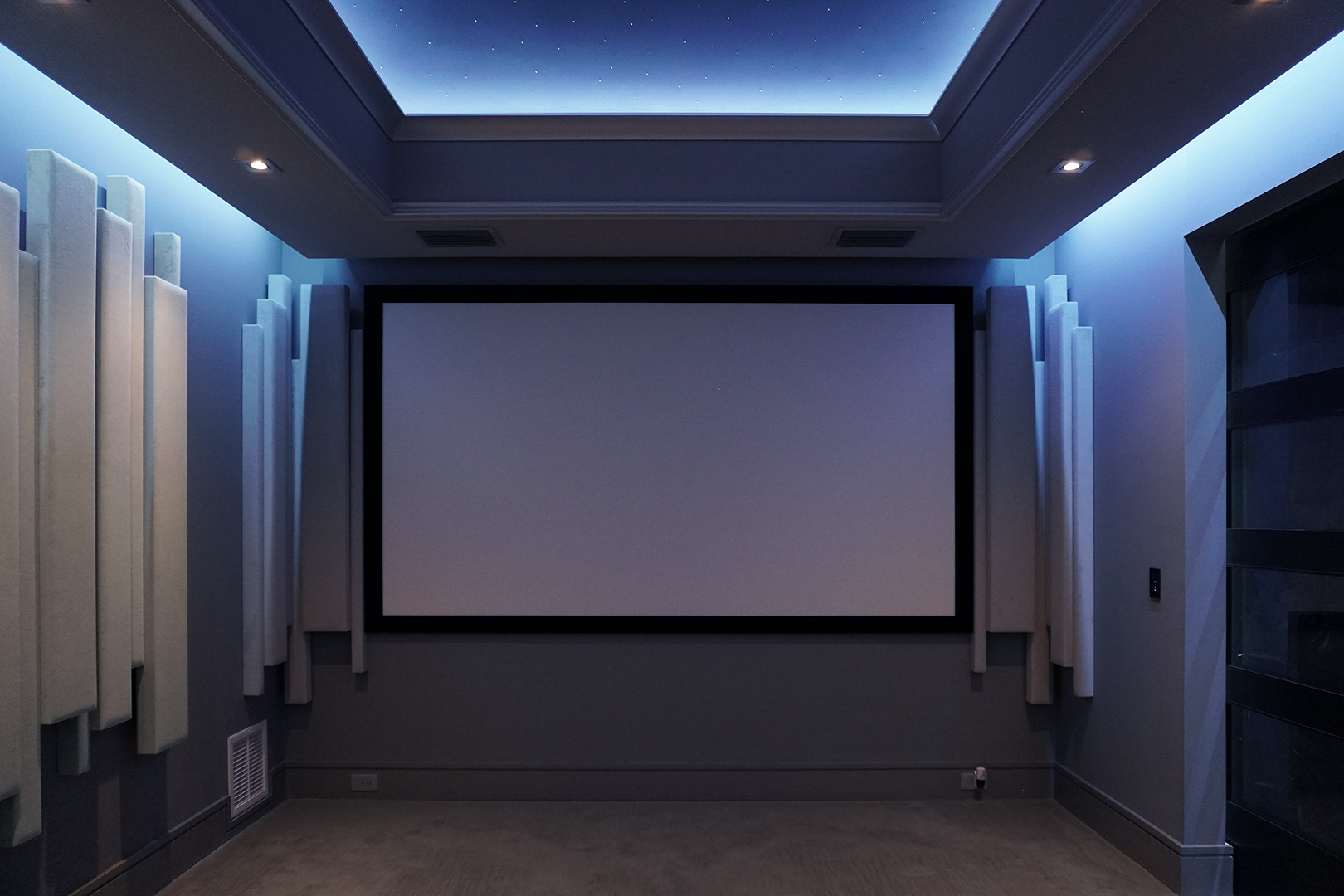
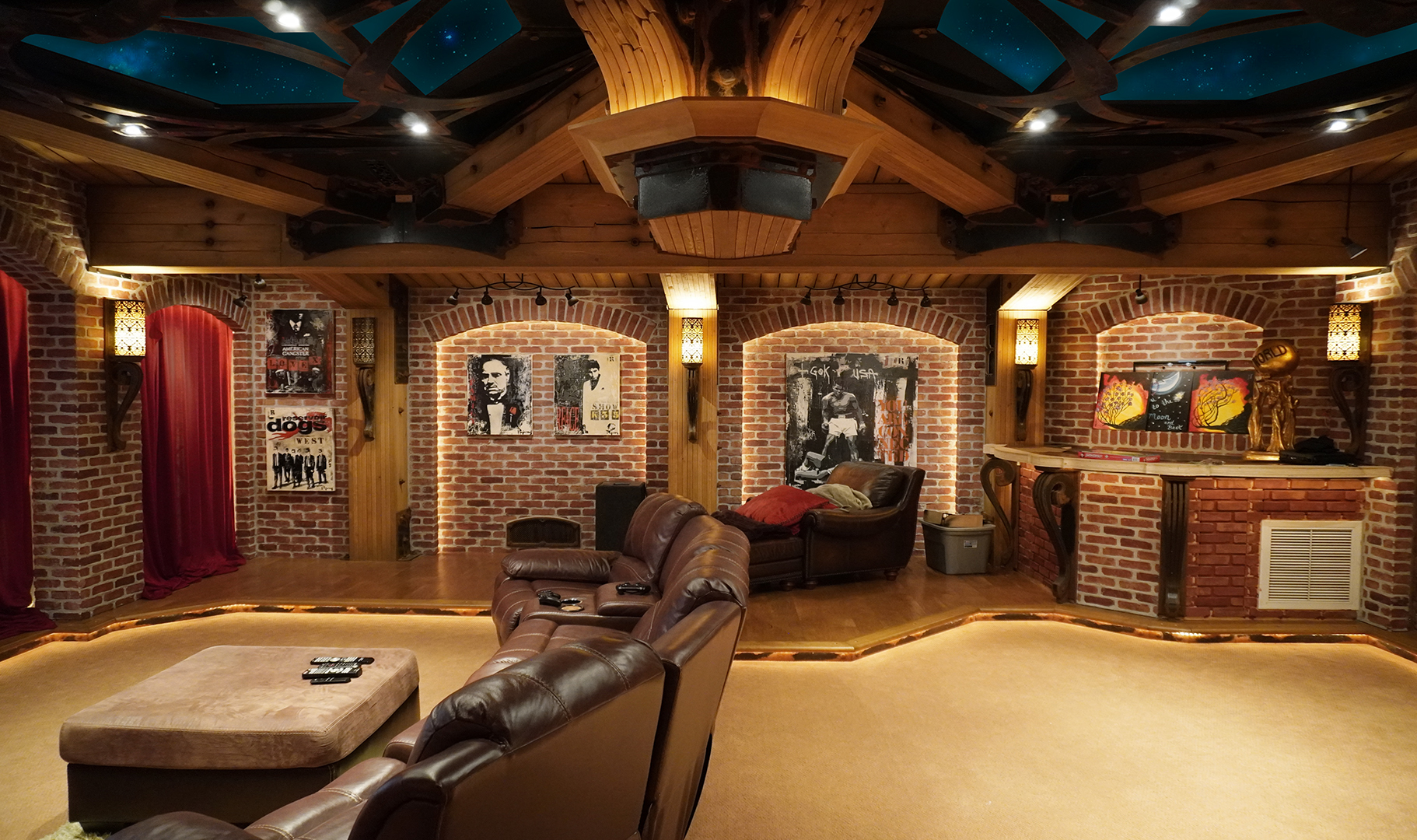
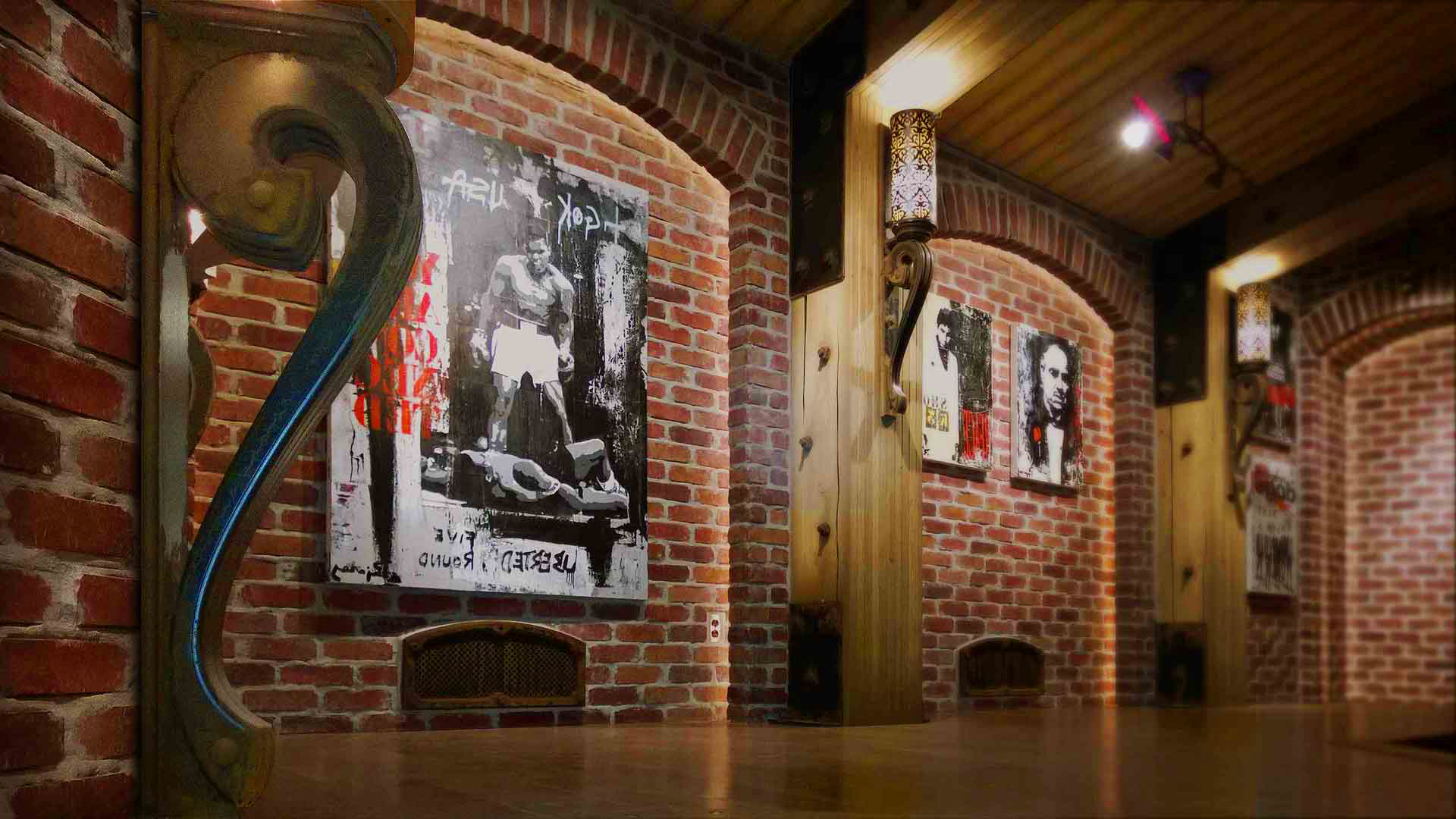
Gallery
How To View
All Devices
Single Tap Image to
Expand/Collapse
Expand/Collapse
Mobile Only
Double Tap Expanded
Image to Zoom In/Out
Image to Zoom In/Out



















